It often begins with a simple glance in the mirror—a bump, a red patch, or an odd-looking spot in your most intimate area. Suddenly, your heart starts racing, and your mind spirals into questions: “Is this normal? Is something wrong with me?” If this sounds familiar, you’re not alone. Genital skin changes are incredibly common, yet many people avoid talking about them because of embarrassment, fear, or uncertainty. The truth is that most of these changes are harmless. Still, some may signal conditions that require medical attention. Knowing how to tell the difference can help you protect your health while avoiding unnecessary panic.
First Things First: Don’t Panic
Before jumping to conclusions, remember that not every bump or discoloration is a sign of infection or disease. Many changes result from everyday factors like shaving, sweating, or wearing tight clothing. Others could stem from mild skin conditions that are easily treatable. The key is understanding what’s normal for your body and recognizing when to see a healthcare provider.
Common and Harmless Causes
One of the most frequent culprits is folliculitis, often known as “shaving bumps.” These appear as small red, white, or pus-filled bumps near the hair follicles. They’re caused by irritation from shaving, friction, or trapped sweat. Most cases clear up with simple care—try warm compresses, skip shaving for a while, and keep the area clean and dry. If the bumps become painful or don’t heal, it’s best to have them checked by a doctor.
Another common issue is sebaceous cysts—smooth, round bumps that form under the skin when oil glands become blocked. They’re typically flesh-colored or slightly yellowish and rarely dangerous. The key is to resist the urge to squeeze them, as that can cause infection. If a cyst becomes swollen or painful, a healthcare professional can safely drain it.
Skin tags and ingrown hairs are also frequent and generally harmless. Skin tags are tiny flaps of extra tissue that appear where friction occurs, while ingrown hairs develop when hair grows back into the skin, creating a small bump that might look irritated. Though they may look alarming, they usually require no treatment unless they cause discomfort. Still, if something feels unusual or changes in appearance, it’s smart to get a medical opinion.
When to Pay Attention: Possible Medical Causes
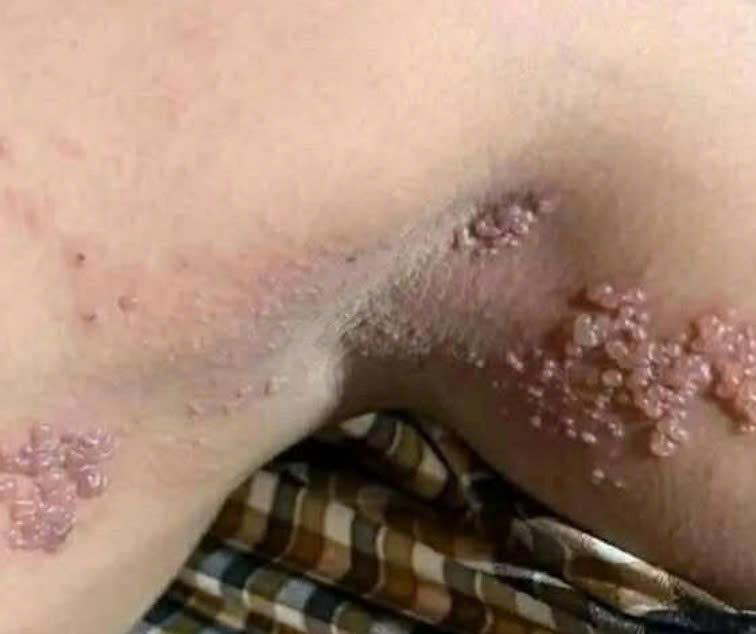
Some genital skin changes can indicate infections or other conditions that need medical care. One of the most common is genital warts, caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). These warts are typically soft, flesh-colored, and can appear singly or in clusters. They may spread through sexual contact, so professional evaluation is necessary. Doctors can provide various treatment options, including topical creams, freezing, or removal procedures.
Genital herpes, caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), is another condition to watch for. It often begins with tingling or burning sensations followed by painful blisters or sores. While there’s no cure, antiviral medications can help manage symptoms and reduce outbreaks. Early diagnosis is important for preventing transmission and minimizing discomfort.
Molluscum contagiosum, a viral skin infection, appears as small, shiny, dome-shaped bumps with a central dimple. It can spread through skin-to-skin contact, including sexual contact. In most cases, it clears up on its own over several months, but seeing a doctor can help prevent spreading it further.
Syphilis is a more serious bacterial infection that can start with a single, painless sore called a chancre. Though it may heal on its own, the bacteria remain in the body and can cause severe complications if untreated. Antibiotic treatment—usually penicillin—is essential to prevent long-term damage.
Lastly, conditions such as lichen sclerosus or lichen planus involve chronic inflammation that causes itchy white patches or purplish flat bumps on the genital skin. These require medical diagnosis and prescription treatments, often involving corticosteroid creams, to manage symptoms and prevent scarring.
When to See a Doctor
It’s crucial to pay attention to warning signs. You should schedule a medical visit if:
-
Bumps or lesions don’t heal within a week or two
-
You experience pain, burning, or unusual discharge
-
Sores bleed, crust, or keep returning
-
You notice any change in color, shape, or size of existing spots
Bringing up these issues might feel uncomfortable, but healthcare providers handle them routinely. Their job isn’t to judge—it’s to help. By seeking advice early, you can prevent potential complications and gain peace of mind.
The Bottom Line: Stay Calm, Stay Aware
Your body changes over time, and sometimes those changes appear in unexpected places. Genital skin differences are common, and many are nothing to worry about. The real risk lies in ignoring your body’s signals or letting embarrassment keep you from asking questions. Most causes are treatable or completely harmless once identified correctly.
So, instead of panicking, pay attention. Educate yourself about what’s normal for you. If something looks or feels off, trust your instincts and talk to a healthcare provider. Your health—and your peace of mind—are too important to leave to guesswork.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Always consult your doctor or healthcare provider about any concerns regarding your health or medications. Never ignore professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you’ve read online.
If you found this article helpful, consider sharing it with family and friends on Facebook to help spread awareness and reduce stigma around this common but often overlooked topic.