Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it’s not life-threatening, it can significantly impact a person’s physical and emotional well-being. Understanding the different types, causes, and treatment options is crucial for managing the condition effectively. If you notice any unusual changes in your skin or suspect you might have psoriasis, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly.
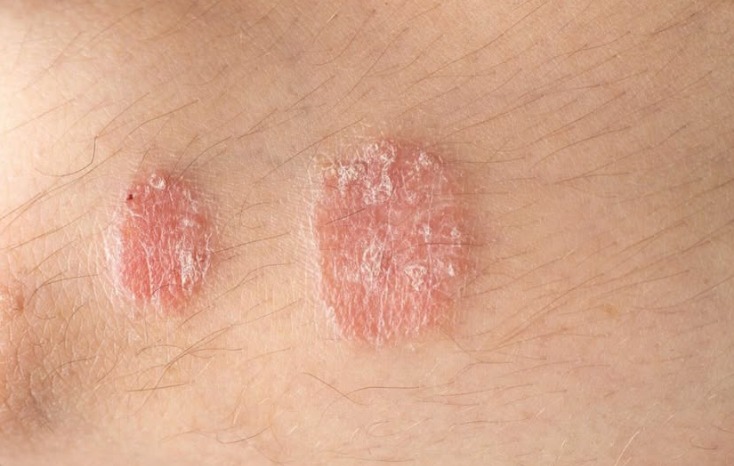
There are several distinct types of psoriasis, each with unique characteristics. Plaque psoriasis is the most common form, presenting as red, raised patches of skin covered with silvery scales. These patches often appear on the scalp, elbows, and knees, causing itching and discomfort. On the other hand, guttate psoriasis shows up as small, pink, drop-shaped spots, usually on the trunk, arms, and legs. These spots are typically thinner and smaller than the lesions seen in plaque psoriasis. Pustular psoriasis primarily affects adults and is marked by red, inflamed skin covered in pus-filled blisters. These blisters may concentrate on the hands and feet or spread across the body. Another variation is inverse psoriasis, which thrives in moist skin folds like under the breasts, around the groin, and in the armpits. It manifests as smooth, shiny, red patches of irritated skin. Lastly, the rare and severe erythrodermic psoriasis resembles an extreme sunburn, causing widespread peeling, intense redness, fever, and general illness. This type is considered a medical emergency and requires immediate intervention.
Despite its dramatic appearance, psoriasis is not contagious. You cannot catch it from someone else through physical contact, shared belongings, or airborne particles. The condition arises from internal factors, primarily linked to the immune system.
The root cause of psoriasis lies in immune system dysregulation. In people with psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, triggering an overproduction of new skin cells. This rapid turnover leads to the buildup of thick, scaly patches on the skin’s surface. Genetics also play a significant role, as psoriasis often runs in families. Research indicates that around 2–3% of cases have a hereditary link, meaning if a parent or grandparent has psoriasis, you may be at higher risk of developing it.
Certain triggers can exacerbate or activate psoriasis symptoms. Excessive alcohol consumption is known to worsen flare-ups, as it can weaken the immune system and interfere with medications. Certain medications, such as lithium, antimalarial drugs, and specific blood pressure medications, have also been linked to psoriasis flare-ups. Additionally, infections like strep throat can activate the immune system, leading to sudden outbreaks, especially in guttate psoriasis.
Diagnosing psoriasis usually begins with a physical examination by a dermatologist. The doctor will carefully inspect the affected skin areas, ask about your family history, and review your overall health profile. In some cases, if the diagnosis is unclear, a skin biopsy may be performed. This involves taking a small skin sample for microscopic analysis to confirm whether psoriasis is the cause of the skin changes.
While there is no cure for psoriasis, effective treatments can significantly manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Topical treatments are often the first line of defense and are applied directly to affected skin areas. These include corticosteroids, which reduce inflammation, vitamin D analogues, which slow down the rapid growth of skin cells, and retinoids, which promote skin renewal. Other topical treatments, like salicylic acid, help remove scales, while moisturizers soothe and hydrate the skin, reducing itchiness and flakiness.
For moderate to severe cases, immunosuppressive drugs are often prescribed. These include methotrexate, which suppresses the immune system to prevent flare-ups, and cyclosporine, which directly targets inflammation. Additionally, biologic medications have revolutionized psoriasis treatment by targeting specific immune pathways responsible for the disease. Another effective option is phototherapy, where controlled exposure to natural sunlight or artificial ultraviolet (UV) light reduces inflammation and slows down skin cell turnover.
It’s essential to understand that psoriasis is a chronic but manageable condition. By identifying triggers, adopting a balanced lifestyle, and using a combination of treatments such as topical medications, immunosuppressive drugs, and phototherapy, individuals can reduce symptoms and prevent frequent flare-ups. However, psoriasis management requires a tailored approach, as the condition can vary greatly from person to person. Consulting a dermatologist is the best way to create a personalized treatment plan.
If you notice persistent red patches, silvery scales, or unusual skin irritation, don’t wait for symptoms to worsen. Early intervention is key to preventing complications and ensuring effective management. Specialized medical centers, such as Vinmec International General Hospital, offer advanced care and expert consultations for psoriasis patients. With the right support and treatment plan, living a fulfilling and comfortable life with psoriasis is entirely possible. Don’t hesitate to seek medical help if you recognize any of these warning signs on your body. Your skin—and overall health—deserve the best care possible.